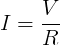Capacitor
What is capacitor
Capacitor is an electronic component that stores electric charge. The capacitor is made of 2 close conductors (usually plates) that are separated by a dielectric material. The plates accumulate electric charge when connected to power source. One plate accumulates positive charge and the other plate accumulates negative charge.
The capacitance is the amount of electric charge that is stored in the capacitor at voltage of 1 Volt.
The capacitance is measured in units of Farad (F).
The capacitor disconnects current in direct current (DC) circuits and short circuit in alternating current (AC) circuits.
Capacitor pictures
Capacitor symbols
Capacitor | ||
Polarized capacitor | ||
Variable capacitor |
Capacitance
The capacitance (C) of the capacitor is equal to the electric charge (Q) divided by the voltage (V):
C is the capacitance in farad (F)
Q is the electric charge in coulombs (C), that is stored on the capacitor
V is the voltage between the capacitor's plates in volts (V)
Capacitance of plates capacitor
The capacitance (C) of the plates capacitor is equal to the permittivity (ε) times the plate area (A) divided by the gap or distance between the plates (d):
C is the capacitance of the capacitor, in farad (F).
ε is the permittivity of the capacitor's dialectic material, in farad per meter (F/m).
A is the area of the capacitor's plate in square meters (m2].
d is the distance between the capacitor's plates, in meters (m).
Capacitors in series
The total capacitance of capacitors in series, C1,C2,C3,.. :
Capacitors in parallel
The total capacitance of capacitors in parallel, C1,C2,C3,.. :
CTotal = C1+C2+C3+...
Capacitor's current
The capacitor's momentary current ic(t) is equal to the capacitance of the capacitor,
times the derivative of the momentary capacitor's voltage vc(t):
Capacitor's voltage
The capacitor's momentary voltage vc(t) is equal to the initial voltage of the capacitor,
plus 1/C times the integral of the momentary capacitor's current ic(t) over time t:
Energy of capacitor
The capacitor's stored energy EC in joules (J) is equal to the capacitance C in farad (F)
times the square capacitor's voltage VC in volts (V) divided by 2:
EC = C × VC 2 / 2
AC circuits
Angular frequency
ω = 2π f
ω - angular velocity measured in radians per second (rad/s)
f - frequency measured in hertz (Hz).
Capacitor's reactance
Capacitor's impedance
Cartesian form:
Polar form:
ZC = XC∟-90º
Capacitor types
| Variable capacitor | Variable capacitor has changeable capacitance |
| Electrolytic capacitor | Electrolytic capacitors are used when high capacitance is needed. Most of the electrolytic capacitors are polarized |
| Spherical capacitor | Spherical capacitor has a sphere shape |
| Power capacitor | Power capacitors are used in high voltage power systems. |
| Ceramic capacitor | Ceramic capacitor has ceramic dielectric material. Has high voltage functionality. |
| Tantalum capacitor | Tantalum oxide dielectric material. Has high capacitance |
| Mica capacitor | High accuracy capacitors |
| Paper capacitor | Paper dielectric material |